- June 16, 2025
- Pankaj Kumar
- 0
Imagine leaving your house unlocked with all your valuables inside. That’s what skipping a Microsoft 365 security audit feels like.
As organizations rely more on cloud tools for collaboration, productivity, and data management, their attack surface expands dramatically. A regular security audit ensures your Microsoft 365 environment is locked down, compliant, and resilient.
This guide covers everything you need — from what to audit and how to prepare, to the tools, scripts, and best practices that help secure your tenant.
What is a Microsoft 365 Security Audit?
A Microsoft 365 security audit is a comprehensive review of your organization’s environment designed to uncover:
-
Security gaps and misconfigurations
-
Compliance and data protection issues
-
Risky user or admin behaviors
Scope of the Audit Includes:
-
User and admin access
-
Data sharing and permissions
-
Email and Exchange protection
-
Device and endpoint security
-
Monitoring and logging configuration
This isn’t just about compliance — it’s your first line of defense against internal and external threats.
Benefits of Regular Security Assessments
Why should you perform regular Microsoft 365 security audits?
-
🔒 Proactive Risk Reduction – Identify and fix weak points before attackers find them.
-
📊 Compliance Readiness – Stay audit-ready for ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR.
-
🔁 Operational Continuity – Avoid downtime caused by security incidents.
-
💡 Security Awareness – Detect shadow admin accounts or unused privileges.
When Should You Perform a Microsoft 365 Security Audit?
While continuous monitoring is ideal, schedule deeper audits:
-
Quarterly – For high-security or regulated industries
-
After major changes – Vendor onboarding or migrations
-
Post-incident – Following a breach or unusual activity
Pre-Audit Preparation
Before you start your Microsoft 365 audit, gather:
-
A cross-functional team (IT, Security, Compliance)
-
List of critical apps and data repositories
-
Access to portals: Microsoft 365 Admin Center, Entra ID, Purview, and Security
Pro Tip: Assign the Global Reader role to auditors for secure, read-only access.
Key Areas to Audit in Microsoft 365
1. Identity and Access Management
-
Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all users and admins.
-
Configure Conditional Access policies to reduce risky sign-ins.
-
Review and clean up guest accounts.
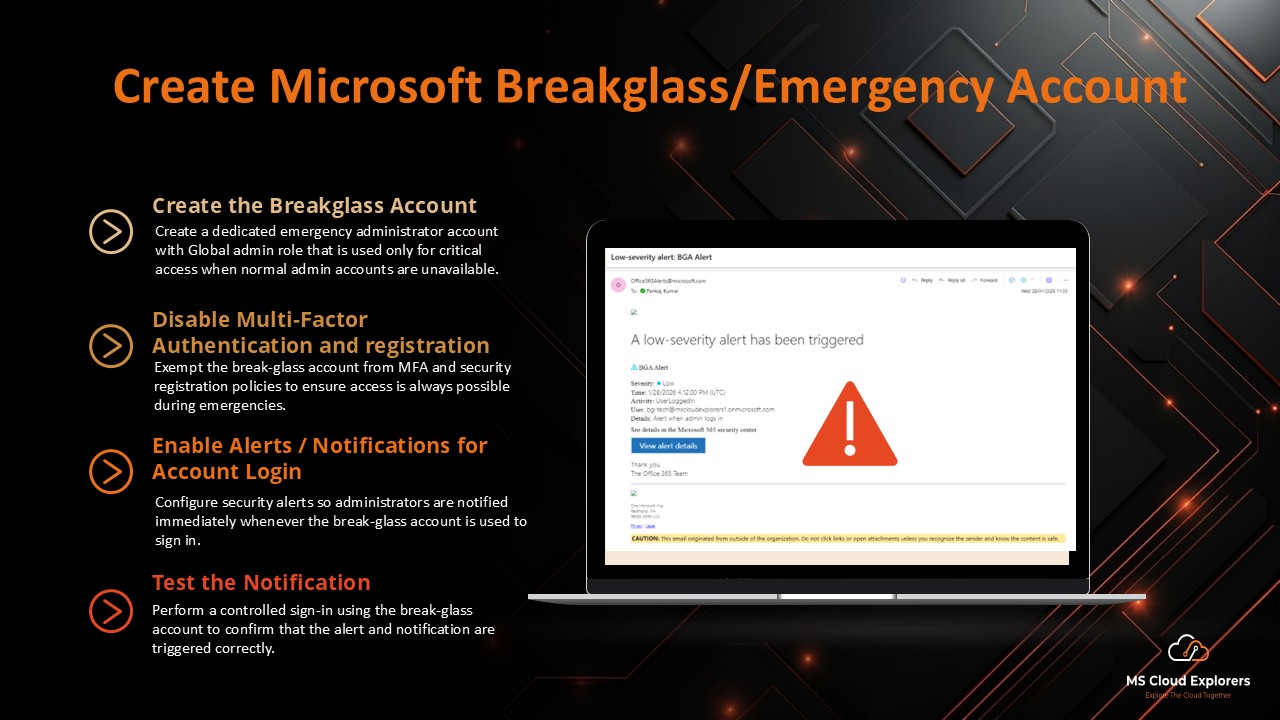
-
Maintain break-glass accounts with monitoring alerts.
🔗 Read the complete guide on Microsoft Entra ID Protection.
2. Licensing and Role-Based Access
-
Verify licenses are assigned only to active users.
-
Limit privileged roles like Global Admin and Exchange Admin.
-
Remove inactive users from admin roles.
Tip: Run PowerShell reports to analyze license usage and access roles. Review the License with the PowerShell script
3. Exchange Online & Email Security
-
Enable Anti-phishing, Anti-spam, and Anti-malware policies.
-
Configure DMARC, DKIM, and SPF for email authentication.
-
Enable mail flow auditing for compliance tracking.
4. SharePoint & OneDrive Sharing Settings
-
Restrict external sharing to trusted domains.
-
Apply sensitivity labels to confidential content.
-
Review for anonymous links that expose data publicly.
5. Microsoft Teams & Collaboration Controls
-
Audit guest and external access policies.
-
Align chat and file sharing settings with compliance rules.
-
Train users on secure collaboration practices.
6. Microsoft Defender for Office 365
-
Enable Safe Links for URL scanning.
-
Turn on Safe Attachments for malware detection.
-
Configure automated threat notifications.
🔗 Check out our guide on Microsoft Defender for Office 365.
7. Data Loss Prevention & Information Protection
-
Apply DLP policies to monitor sensitive data (financial, health).
-
Map sensitive information types to policies.
-
Train users on sensitivity labels and data classification.
🔗 Learn how to set up DLP policies.
8. Audit Logs and Activity Reports
-
Ensure Unified Audit Log is enabled (minimum 180 days).
-
Configure activity alerts for mass deletions or permission changes.
9. Microsoft Entra ID Protection
-
Configure user risk and sign-in risk policies.
-
Block or force password reset for high-risk users.
-
Enable automated remediation for compromised accounts.
🔗 Complete guide on Microsoft Entra ID Overview
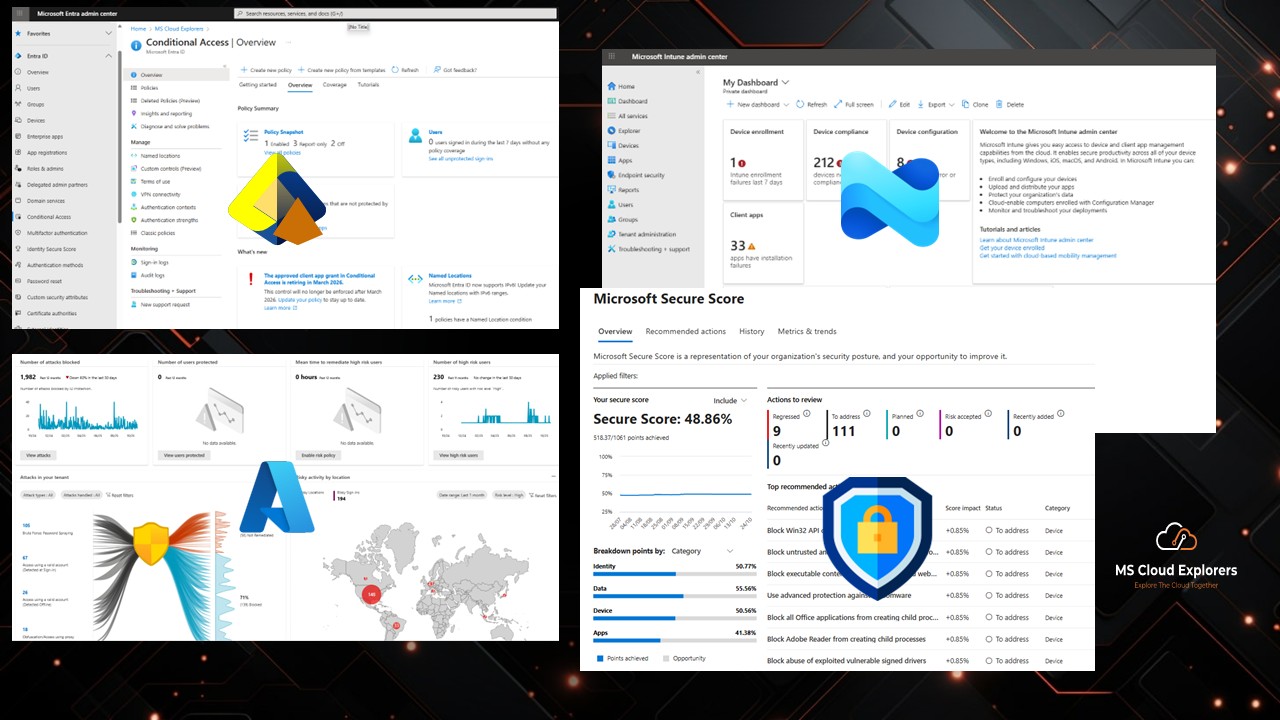
10. Endpoint Security & Intune Compliance
-
Ensure all corporate devices are enrolled in Intune.
-
Apply mobile application policies for Teams, Outlook, and OneDrive.
-
Enforce compliance using Conditional Access.
🔗 Explore our full guide on Microsoft Intune Compliance.
Top Tools for Microsoft 365 Security Auditing
Microsoft Secure Score
-
Get a security score (0–100) with improvement insights
-
Track progress and historical trends
🔗 Read the complete guide on Microsoft Secure Score
Third-Party Tools
- SysKit, AvePoint, Admin Droid, Cloud Capsule, for deeper reporting and alerting
- Automated policy monitoring and license usage analysis
📑 Creating a Security Audit Checklist
A working checklist helps you standardize the audit. Here’s a quick example:
| Area | Item to Check | Status |
| MFA | Enabled for all users | ✅ |
| DLP | Policy for Credit Card numbers | ❌ |
| Admin Roles | Global Admin count | 5 (should be < 3) |
| Audit Logs | Enabled | ✅ |
Post-Audit Action Plan
Once the audit is complete:
- ✅ Prioritize findings by risk
- 🧑💻 Assign ownership and remediation timelines
- 🔁 Review Secure Score monthly
- 🧾 Set a quarterly audit review calendar
Conclusion
A Microsoft 365 security audit isn’t a compliance checkbox — it’s your roadmap to a secure and resilient cloud environment.
By auditing regularly, empowering admins, and following a structured approach, you protect your organization from data leaks, account takeovers, and compliance pitfalls.
Don’t wait for an incident — start your next Microsoft 365 security audit today.
FAQs
1. How often should I audit my Microsoft 365 tenant?
At minimum, quarterly. More frequently for high-risk industries or post-breach scenarios.
2. Is Secure Score enough for a full audit?
No. It’s a great starting point but doesn’t cover all compliance or configuration nuances.
3. Can I automate M365 audits?
Yes, with tools like Microsoft Graph API, PowerShell scripts, and third-party platforms like SysKit or AvePoint.
4. Do I need third-party tools for a successful audit?
Not necessarily. Microsoft’s built-in tools are robust, but third-party tools add depth, reporting, and automation.
5. What’s the difference between a security audit and a compliance audit?
Security audits focus on risk and technical misconfigurations, while compliance audits align practices to standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO.
Related Links:-
Enjoyed the article?
We’d love to hear your thoughts—share your comments below!
For more insights, guides, and updates from the Microsoft ecosystem, be sure to subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on LinkedIn. Stay connected and never miss out on the latest tips and news!