
In today’s mobile-first, cloud-powered world, managing and securing devices is paramount for businesses. Microsoft Endpoint Manager (MEM), featuring the robust Microsoft Intune platform, offers unparalleled capabilities for managing endpoints and securing corporate data. This guide introduces you to MEM’s key features, benefits, and how it supports modern IT needs in 2025.
What Is Microsoft Endpoint Manager?
Microsoft Endpoint Manager is a unified management platform designed to manage endpoints — such as laptops, desktops, mobile devices and even virtual/cloud endpoints — across your organization. It seamlessly integrates tools like Intune (cloud-based endpoint management) and Configuration Manager (on-premises management) to provide comprehensive device management and security.
Why Endpoint Manager matters
-
Unification of device management (cloud + on-premises).
-
Enables modern workforces (remote/hybrid/BYOD) with central visibility.
-
Adds new intelligence and automation features (e.g., AI-driven insights) through Intune.
-
Faster OS version support (day-zero) for Apple, Windows etc.
Key Features of Microsoft Endpoint Manager
Device Management:
-
Cross-Platform Support: Manage Windows, macOS, iOS, Android (company-owned and BYOD).
-
Automated Enrollment: Onboarding devices with autopilot/enrollment flows so they arrive pre-configured and policy-ready.
-
Unified Console: Single pane of glass for device state, compliance, app deployments — removing silos.
App Management:
-
Centralised Deployment: Push Microsoft 365 apps, third-party software, custom business apps from MEM.
-
App Protection Policies: Even on unmanaged devices (BYOD), protect corporate data inside apps by restricting copy/paste, Save-As, etc.
-
Example: In June 2025 release, application protection policies got enhanced to cover more apps and data flows.
-
-
PowerShell Script Support for Win32 App Deployment: As of September 2025, you can upload PowerShell scripts in Intune’s Enterprise App Catalog for app installs.
Zero Trust Security:
-
Conditional Access: Only allow devices and users who meet compliance rules (location, device health, app state) to access corporate resources.
-
Multifactor Authentication (MFA): Integrates with Azure AD to require multiple verification steps.
-
Endpoint Privilege Management (EPM): New rules to prevent elevation attacks (deny certain files from running elevated).
Compliance Policies:
-
Security Standards Enforcement: Define compliance policies (e.g., encryption, password strength, minimum OS version) to prevent risky devices from accessing corporate data.
-
Real-Time Monitoring & Insights: Want greater oversight? The “Vulnerability Remediation Agent” (public preview) uses data from Microsoft Defender to recommend settings—now in Intune.
-
Day-Zero OS Version Support: For example, support for windows version 25H2 settings catalog added in Oct 2025.
Integration with Azure AD & other Microsoft Services
-
Streamlined Identity Management: Leverage Azure Active Directory for unified identity & access management across devices and apps.
-
Single Sign-On (SSO): Users log in once to access a range of applications.
-
Security Ecosystem Integration: With Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, Azure AD, Windows Autopilot—all working together.
Check out the guides on how to integrate apps with Azure AD.
What Is Microsoft Intune?
Microsoft Intune is the cloud-centric agent of MEM: a mobile device management (MDM) and mobile application management (MAM) platform. Key capabilities:
-
Control Access: Ensure only authorised users + compliant devices gain access.
-
Enforce Policies: Encryption, password rules, device restrictions, etc.
-
Deploy Apps: Seamlessly deploy and update apps across devices, whether corporate-owned or BYOD.
Latest Intune Updates (2025) to highlight
-
May 2025: Multiple admin approvals for sensitive remote actions; Linux server global exclusions; Unattended remote help for corporate Android devices.
-
August 2025: App Control for Business (general availability) enabling granular targeting of App Control policies rather than tenant-wide only.
-
September 2025: PowerShell script support for Win32 app installation; Android Intune Company Portal older versions support ended; Vulnerability Remediation Agent updates.
These updates show how Intune is moving beyond simply device management toward automation, security-first configuration, and insight-driven management.
Why Choose Microsoft Endpoint Manager?
Benefits for Businesses
-
Enhanced Security: With Zero Trust, integrated identity + device controls, and deeper insights, you better protect sensitive data.
-
Centralized Management: One console for all endpoints saves IT time and reduces complexity.
-
Flexibility for Hybrid Workforces: Whether remote, on-site, BYOD or corporate-owned, MEM supports them all.
-
Scalability & Future-proofing: MEM scales from smaller organizations to large enterprises; with frequent updates like those above, you stay current.
Real-World Use Cases
-
Remote Workforce Enablement: Secure employees accessing corporate apps/data from anywhere.
-
BYOD Management: Allow personal devices in work scenarios while protecting corporate data via app protection policies.
-
Streamlined App Deployment: Deploy/update apps across thousands of endpoints efficiently — e.g., via PowerShell script support in Intune.
-
Device Lifecycle Management: New devices enroll automatically, policies apply out-of-box experience, secure devices from day-one. (e.g., patching during OOBE for Windows).
Getting Started with Microsoft Endpoint Manager
Here’s a high-level roadmap to implement MEM + Intune effectively:
-
License & Sign-Up
-
Acquire appropriate licensing: Intune is included in Microsoft 365 E3/E5, EMS E3/E5, Microsoft 365 Business Premium. Intune Licensing
-
Ensure you have the right roles/permissions for setup.
-
-
Device Enrollment Setup
-
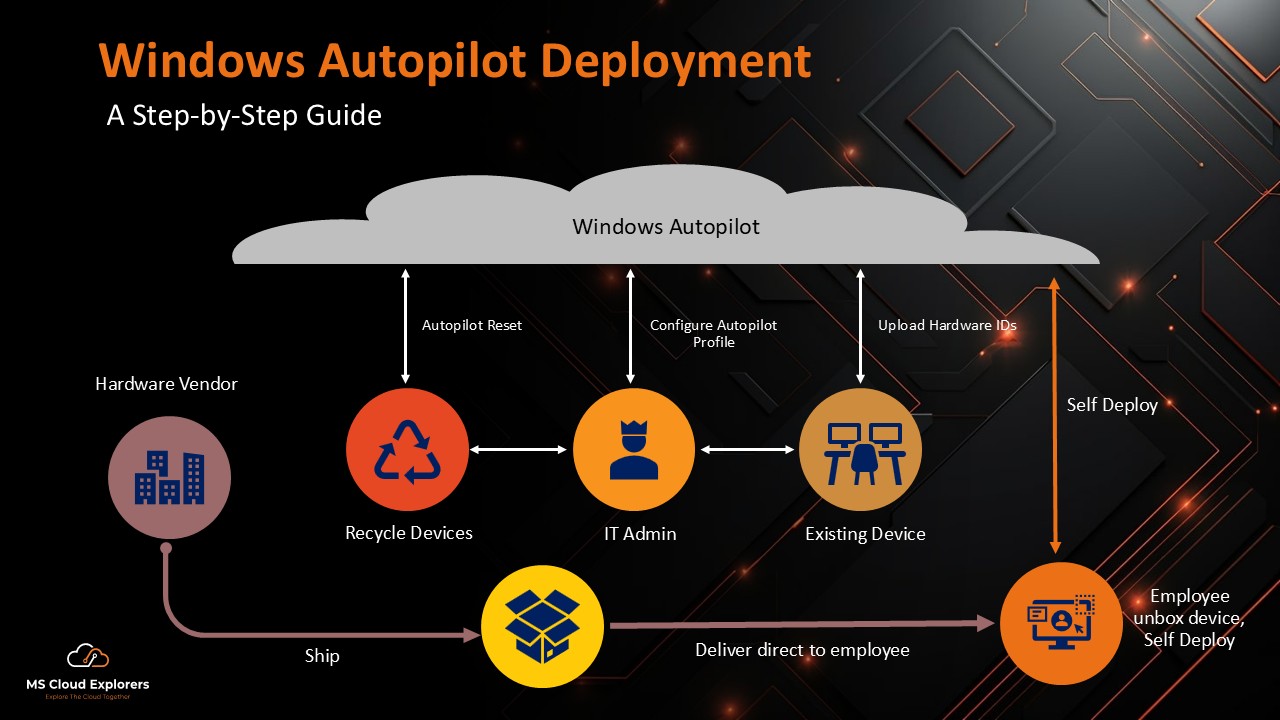
Configure enrolment processes for Windows (via Autopilot), iOS, Android (Android Enterprise), macOS.
-
Define device groups, Autopilot profiles, zero-touch configuration.
-
-
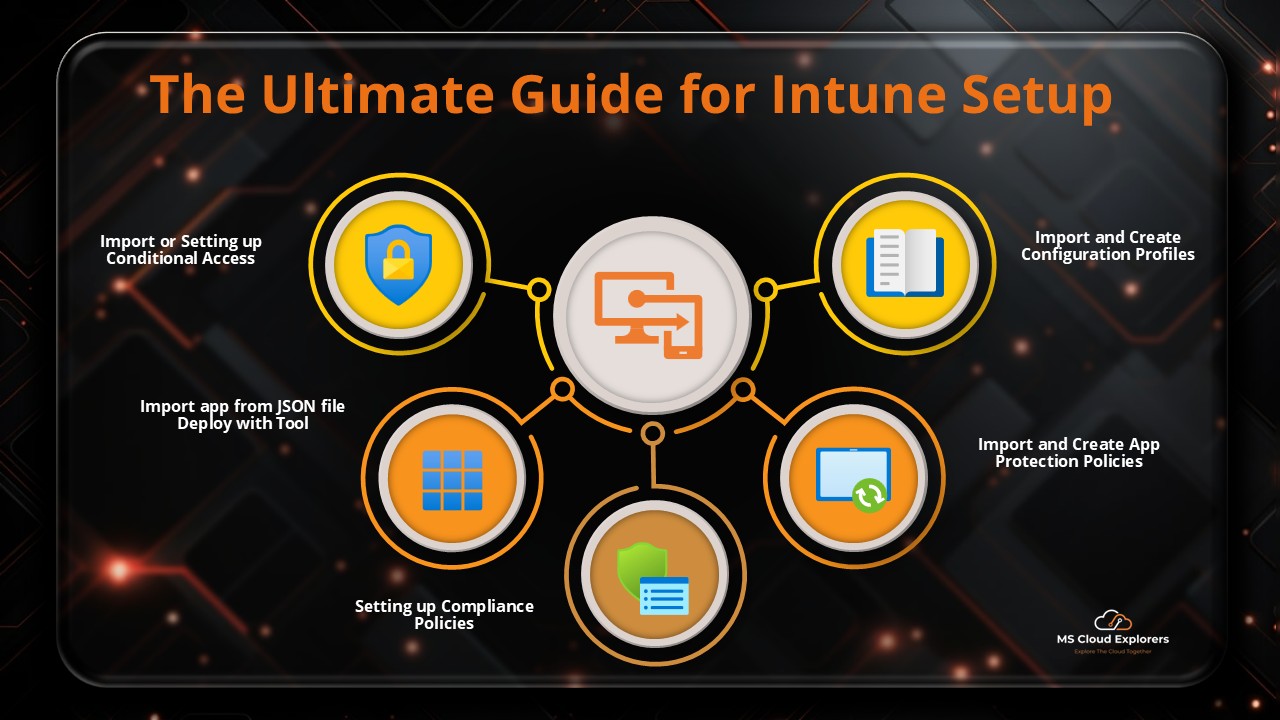
Define Policies
-
Security & compliance policies: encryption, password complexity, OS version minimums.
-
Device configuration profiles (Settings Catalog etc) aligned to your security strategy.
-
Note: Intune now supports filtering by policy type in the settings catalog.
-
-
App protection policies for BYOD / unmanaged devices.
-
-
Deploy Applications
-
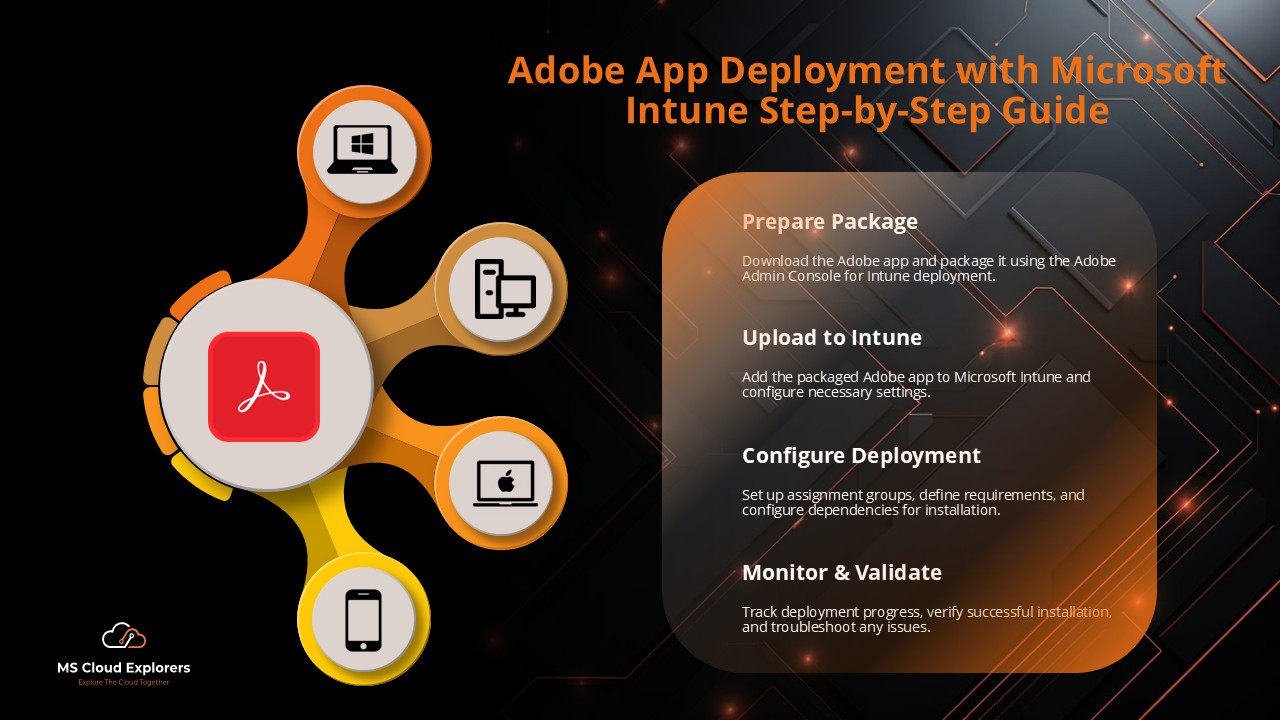
Add applications (Microsoft 365 apps, LOB apps, third party) to the MEM portal.
-
Utilize new capabilities such as PowerShell script installation for Win32 apps.
-
Roll-out stepwise: pilot groups, staging, full deployment — especially with App Control for Business’s targeting.
-
-
Monitor, Adjust & Improve
-
Regularly review device compliance dashboards, alerts, audit logs.
-
Take advantage of Vulnerability Remediation Agent to receive actionable recommendations.
-
Update OS version support (e.g., Windows 11 version 25H2 settings added).
-
Iterate: refine device groups, enrollment flows, policies as business needs evolve.
-
Conclusion
Microsoft Endpoint Manager (MEM) paired with Microsoft Intune is now more essential than ever for organizations that want to simplify IT operations, enhance security, and support remote/hybrid workforces. With frequent updates in 2025 — AI-driven insights, day-zero OS support, targeted app control — the platform is continuously evolving. By steadily deploying its capabilities, your organization can drive digital transformation, strengthen security posture, and streamline endpoint operations.
FAQs
Q1: What’s the difference between Configuration Manager and Co-Management?
-
Configuration Manager (SCCM): On-premises tool to manage Windows devices, with deep control of configurations and deployments.
-
Co-Management: A hybrid scenario where devices are simultaneously managed by Configuration Manager and Intune, enabling a transition path to cloud-based management while retaining on-premises capabilities.
Q2: How does Microsoft Intune support app management?
Intune allows administrators to add, assign, configure, and protect apps across various devices — including Microsoft 365 apps, third-party apps, custom line-of-business (LOB) apps. It supports both managed devices and unmanaged/BYOD scenarios through App Protection Policies, for example restricting data sharing on unmanaged devices. (See June 2025 updates for expanded app protection).
Q3: Can Intune manage devices without user intervention?
Yes. Enrolment methods such as Windows Autopilot allow provisioning of new devices with required settings and apps out-of-the-box, significantly reducing manual setup. Additionally, as of 2025, you can enable patches during OOBE so devices are up-to-date before the user first logs in.
Q4: How does Intune integrate with other Microsoft services?
Intune integrates seamlessly with Azure Active Directory (identity & access), Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (endpoint protection + vulnerability data), Microsoft 365 (productivity apps), and Autopilot (device lifecycle). This integration provides a unified, secure environment for managing users, devices, and applications across the organization.
Related Links:-
Enjoyed the article?
We’d love to hear your thoughts—share your comments below!
For more insights, guides, and updates from the Microsoft ecosystem, be sure to subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on LinkedIn. Stay connected and never miss out on the latest tips and news!


4 comments on “Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune): Comprehensive Beginner’s Guide”