
- October 21, 2025
- Pankaj Kumar
- 2
As cyber threats grow in sophistication, organizations need intelligent, cloud-driven protection that goes beyond traditional antivirus. Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (MDE) is an enterprise-grade endpoint security platform offering threat prevention, detection, investigation, and automated response.
In this 2025 guide, we’ll explore the architecture, key features, licensing plans, and deployment steps of Microsoft Defender for Endpoint — helping IT administrators and security teams strengthen their organization’s cybersecurity posture.
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Architecture
MDE operates on a cloud-based architecture tightly integrated with the Microsoft 365 ecosystem, delivering unified visibility and real-time protection across all managed endpoints
1. Cloud-Based Security Services
- Microsoft Threat Intelligence – Analyses trillions of global signals daily using AI and machine learning to identify emerging threats.
- Microsoft Security Graph – Correlates data from endpoints, emails, identities, and cloud applications to generate actionable insights.
- Microsoft Defender XDR – Integrates telemetry from Defender for Office 365, Defender for Identity, and Defender for Cloud to provide end-to-end security visibility.
2. Endpoint Sensors and Agents
Each endpoint runs a lightweight MDE sensor that continuously monitors behavior, collects telemetry, and sends it securely to Microsoft’s cloud for analysis. This enables real-time threat detection and response without performance degradation.
3. Integration with Microsoft Security Solutions
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint integrates seamlessly with:
- Microsoft Defender for Office 365 (email and collaboration app security)
- Microsoft Intune (device management and compliance)
- Microsoft Defender for Identity (identity threat protection)
- Microsoft Sentinel (SIEM/SOAR for advanced threat correlation)
- Microsoft Defender for Cloud (cloud workload protection)
4. Multi-Platform Coverage
MDE supports Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android, and IoT devices — providing consistent protection across hybrid environments.
Update (2025):
- Linux ARM64-based servers are now fully supported.
- Android 8/9 support ended; Android 10+ is now required.
Key Features of Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
1. Threat & Vulnerability Management
- Detects misconfigurations, missing patches, and outdated software.
- Prioritize vulnerabilities based on real-world exploitability.
- Integrates with Intune for automated remediation workflows.
2. Attack Surface Reduction (ASR)
- Minimizes attack vectors by blocking malicious scripts, ransomware behaviors, and untrusted macros.
- Includes Web Protection, Network Protection, and Exploit Guard policies.
- Supports “Block use of copied or impersonated system tools” rule introduced in 2025.
3. Next-Generation Protection
- Uses AI and behavioral analytics to identify and block ransomware, file-less malware, and zero-day exploits.
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint achieved 100% tamper-protection certification in the 2025 AV-Comparatives Anti-Tampering Test.
4. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
- Provides deep forensic visibility and incident timelines.
- Detects suspicious activities, lateral movement, and privilege escalations.
- Offers automatic attack disruption, isolating compromised assets instantly.
5. Automated Investigation & Remediation (AIR)
- Leverages AI-driven automation to investigate alerts and remediate threats with minimal admin input.
- Significantly reduces Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time to Respond (MTTR).
6. Microsoft Threat Experts
- A managed threat-hunting service that delivers proactive investigation and guided incident response.
7. Mobile Threat Defense (MTD)
- Protects iOS and Android endpoints from phishing, malicious apps, and device compromise.
8. Exposure Management & Attack Path Analysis (New for 2025)
- Provides a unified view of device exposure scores.
- Uses AI to identify critical attack paths and recommends mitigation strategies.
9. Industry Recognition
Microsoft was named a Leader in the 2025 Gartner Magic Quadrant for Endpoint Protection Platforms — marking its sixth consecutive year of leadership.
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Licensing Plans
Microsoft offers flexible licensing to fit different organization sizes and security needs.
|
Feature |
Defender for Endpoint P1 |
Defender for Endpoint P2 |
Defender for Business |
|
Attack Surface Reduction |
✅ |
✅ |
✅ |
|
Next-Gen Protection |
✅ |
✅ |
✅ |
|
Endpoint Detection & Response |
❌ |
✅ |
✅ |
|
Automated Investigation & Remediation |
❌ |
✅ |
✅ |
|
Microsoft Threat Experts |
❌ |
✅ |
❌ |
Defender for Endpoint Plan 1 (P1)
- Next-gen antivirus protection
- Attack Surface Reduction policies
- Web content filtering and network protection
- Integration with Microsoft Defender portal
Best for: Businesses seeking strong, cost-effective endpoint protection without advanced EDR.
Defender for Endpoint Plan 2 (P2)
- Includes all P1 features + EDR, AIR, TVM, and Microsoft Threat Experts access.
- Offers Automatic Attack Disruption and Exposure Management (2025 updates).
Best for: Enterprises needing full-scale, AI-driven endpoint security.
Microsoft Defender for Business
- Tailored for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs).
- Combines core protection from P1 + simplified EDR in an easy-to-use interface.
How to Deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (Step-by-Step)
Step 1: Enable Defender for Endpoint in Microsoft 365
- Log in to the Microsoft Defender Security Center.
- Navigate to Settings > Endpoints > Onboarding.
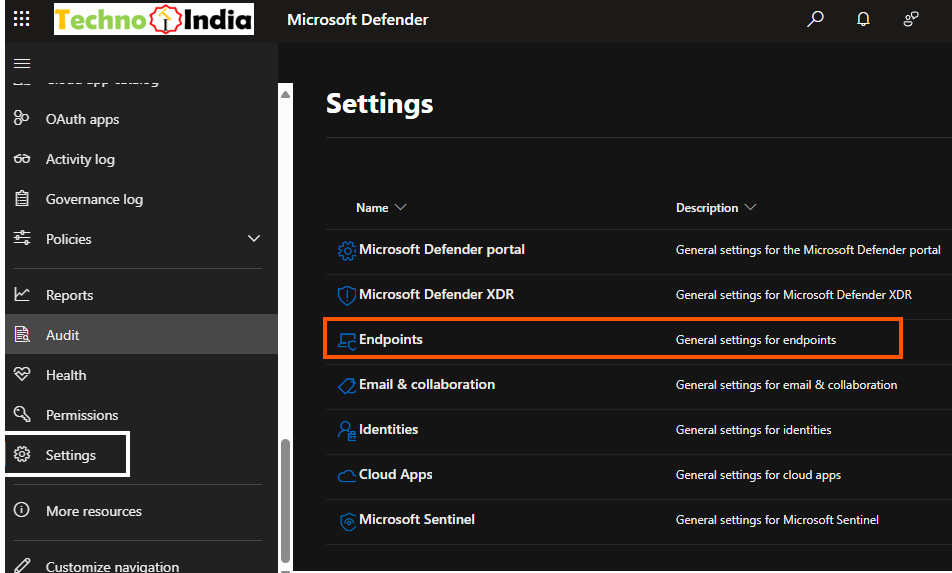
- Choose your deployment method (GPO, Intune, SCCM, etc.).
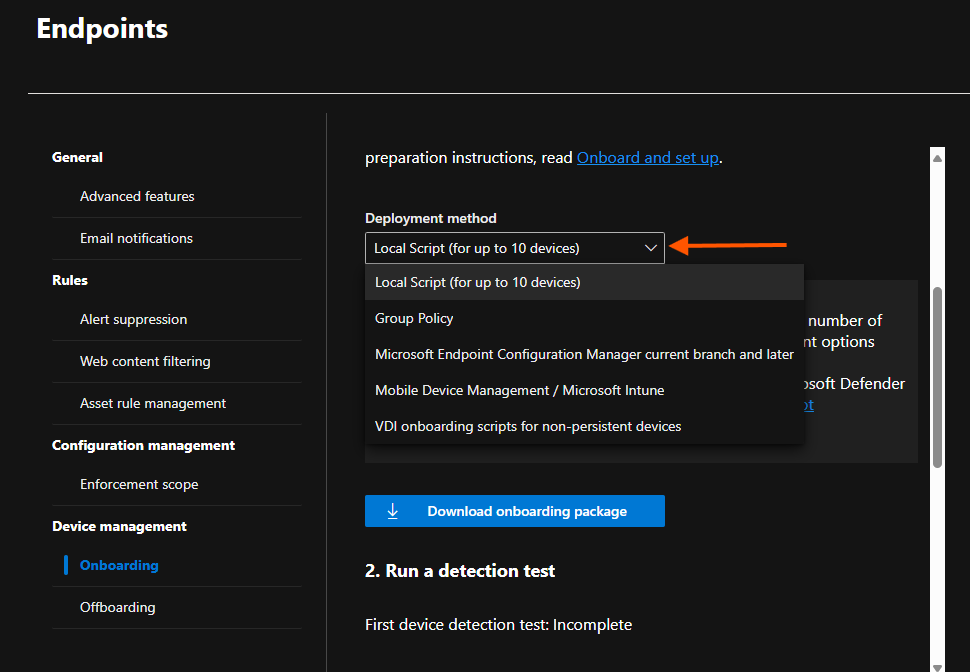
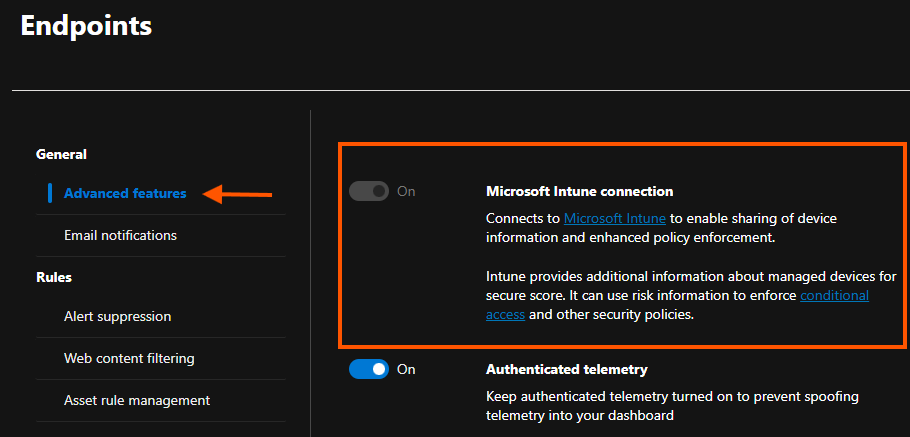
- If you have Intune implemented, you can onboard devices through Intune by enabling the Intune connection in the Advanced Feature Settings.
- Deploy the onboarding script to your endpoints.
Step 2: Configure Security Policies
- Set up Attack Surface Reduction rules.
- Enable Next-Gen Protection policies.
- Configure Endpoint Detection & Response settings.
- Enable Exposure Management to proactively identify and patch high-risk devices
Step 3: Monitor, Investigate & Respond
- Use the Defender portal dashboard for real-time insights.
- Investigate alerts with EDR and AIR tools.
- Quarantine compromised devices and block malicious files.
- Review Secure Score for Devices regularly to measure protection health.
Step 4: Continuous Optimization
- Keep Defender agents up to date (latest engine version ≥ 10.8797).
- Verify mobile device compliance (Android 10+ requirement).
- Update ASR rules and policies as new threats emerge.
- Review reports in Microsoft Sentinel or Defender XDR for cross-domain correlations.
Conclusion
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint delivers comprehensive endpoint protection powered by Microsoft’s global threat intelligence and AI analytics. Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, Defender for Endpoint helps you detect, investigate, and remediate advanced threats across all devices.
By combining Next-Gen Protection, EDR, Automated Response, and Exposure Management, MDE stands as one of the most complete endpoint security platforms of 2025 — trusted globally to protect hybrid environments and critical data.
FAQs
- What is Microsoft Defender for Endpoint used for?
It’s a cloud-powered endpoint security platform that protects devices from malware, ransomware, phishing, and advanced persistent threats. - Can Microsoft Defender for Endpoint replace traditional antivirus?
Yes. MDE combines next-gen antivirus, EDR, and automated threat remediation — going beyond signature-based detection. - How does Microsoft Defender for Endpoint detect threats?
It leverages AI, behavioral analytics, and global threat intelligence (over 84 trillion daily signals) to identify, analyze, and respond to attacks. - What’s the difference between Defender for Endpoint P1 and P2?
P1 offers core protection (AV + ASR), while P2 adds EDR, Threat Analytics, and Automated Remediation for advanced threat hunting. - How do I deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint?
Deploy via Intune, Group Policy, or SCCM, onboard devices through the Defender portal, and monitor activity from a unified dashboard.
Related Articles
Enjoyed the article?
We’d love to hear your thoughts—share your comments below!
For more insights, guides, and updates from the Microsoft ecosystem, be sure to subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on LinkedIn. Stay connected and never miss out on the latest tips and news!

















Awesome guide! Just wondering — does Defender for Endpoint also work on mobile devices, or is it just for PCs?
Thanks for the comment! Yes, Microsoft Defender for Endpoint supports mobile devices too — including Android and iOS. You’ll need to onboard them through Microsoft Intune or another supported MDM. Let us know if you’d like a step-by-step guide for mobile setup!