
As an experienced Microsoft Admin, you’ve likely come across the term “Endpoint Privilege Management” (EPM) — but you might be wondering how it differs from similar concepts like Privileged Identity Management (PIM). While PIM focuses on elevating access for privileged accounts, EPM is specifically designed to address the unique needs of managing administrative rights within Intune-managed environments.
In today’s rapidly evolving IT landscape, most organizations provide users with standard access to their devices, limiting administrative privileges to enhance security. However, there are times when users need to install or configure apps that require elevated rights. Deploying apps directly from Intune can be a lengthy process, requiring rigorous testing and validation before rolling them out across the organization.
With Endpoint Privilege Management in Microsoft Intune, users can easily request app installations or privilege elevation, while Intune admins can review, approve, or deny requests directly from the Intune portal. This streamlined process helps enforce the principle of least privilege, reduces the administrative burden on IT teams, and minimizes security risks.
In this blog, I’ll walk you through what Endpoint Privilege Management is, how it works, and the steps to configure it in your Intune deployment. Whether you’re an IT admin, security manager, or tech leader, mastering EPM will enable you to keep your users productive while reinforcing your organization’s security posture.
Why Endpoint Privilege Management Matters
Many organizations still grant users permanent local admin rights — a dangerous practice that increases the risk of:
- Malware infections
- Accidental system misconfigurations
- Compliance violations during audits
Microsoft Intune’s Endpoint Privilege Management (EPM) addresses these risks by granting just-in-time admin rights only when needed, with full control, policy-based targeting, and audit visibility.
What is Microsoft Intune?
Microsoft Intune is a cloud-based endpoint management solution within the Microsoft Endpoint Manager suite. It enables organizations to:
- Manage devices, applications, and users securely
- Enforce compliance policies
- Protect corporate data from unauthorized access
- Streamline IT administration through central control
Why it’s essential today: With hybrid and remote work becoming the norm, IT teams require a unified and secure platform to manage devices anywhere. Intune integrates deeply with Microsoft’s security ecosystem, making it an ideal solution.
Want to learn more? Browse our other articles on Microsoft Intune.
What Is Endpoint Privilege Management (EPM)?
Endpoint Privilege Management is a feature in Microsoft Intune that controls and elevates user privileges on-demand, eliminating the need for permanent admin rights.
- PIM – Manages privilege elevation for accounts and identities
- EPM – Manages privilege elevation for applications and device-level actions
Key Benefits of EPM
- Reduced Attack Surface – No always-on admin accounts for attackers to target
- Just-in-Time Access – Temporary elevation for specific tasks
- Granular Policy Control – Target by user, device, application, or folder path
- Full Audit Logging – Every elevation request is recorded for compliance
- Improved Productivity – Reduces IT intervention delays for end-users
Challenges Without EPM
Organizations without EPM often face:
- Over-provisioned admin rights
- Limited visibility into privileged actions
- Increased compliance risks during audits
- Higher exposure to malware attacks
EPM and the Zero Trust Model
In traditional environments, many users operated with local admin rights — an open invitation for security breaches.
Zero Trust changes this by granting minimum access, for the shortest necessary time, with ongoing verification.
EPM enforces Zero Trust by ensuring privilege elevation is:
- Temporary
- Policy-driven
- Fully audited
Core Features of EPM in Microsoft Intune
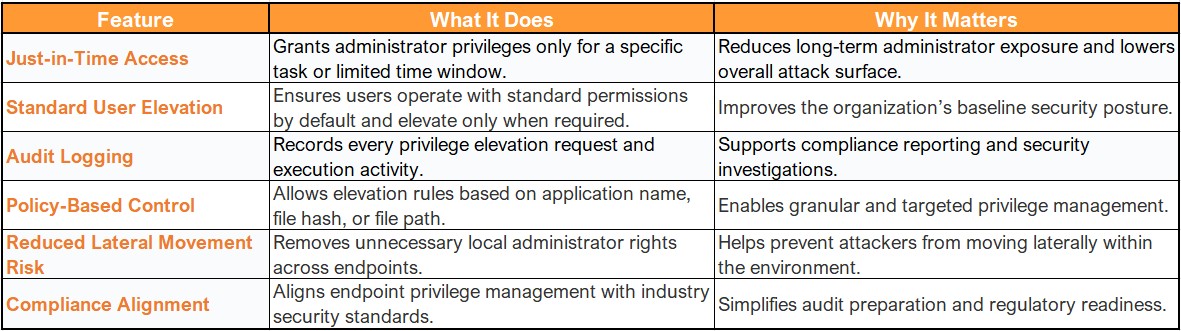
Prerequisites for Deploying EPM
Before enabling EPM, ensure:
- Device Enrollment – Devices must be enrolled in Intune
- Directory Join – Devices are joined to Microsoft Entra ID (cloud or hybrid)
- Supported OS – Windows 10/11 Enterprise or Education (64-bit)
- Licensing – Either:
- Microsoft Intune Suite
- EPM Add-on license for Microsoft 365
How to Configure Endpoint Privilege Management in Intune
- Login to the Intune Admin Portal
- Sign in with Intune Administrator access.
- Navigate to Endpoint Security
- Go to Endpoint Security > Endpoint Privilege Management.
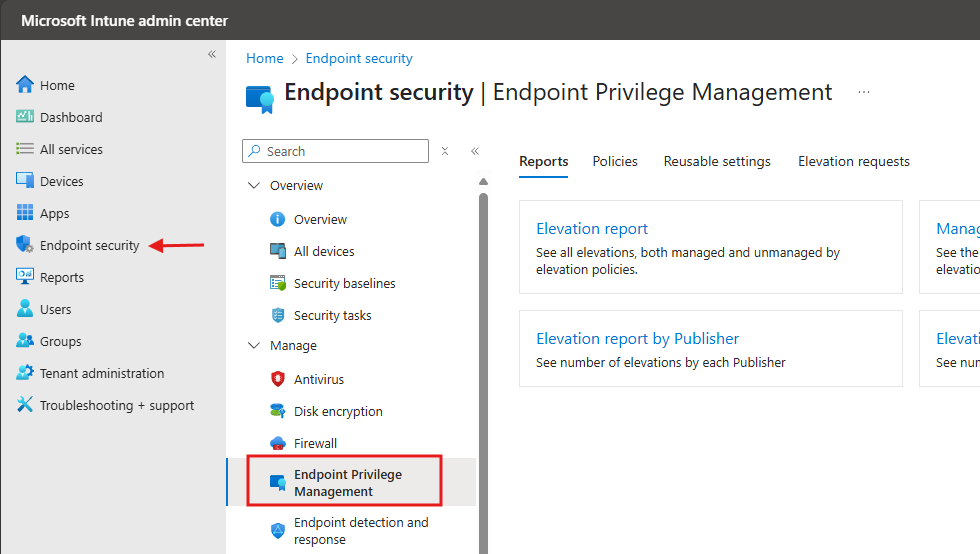
- Go to the Policies Tab
- Click on the Policies tab at the top and select Create Policy.
- Create a New Elevation Policy
- Platform: Windows
- Profile Type: Elevation Settings Policy
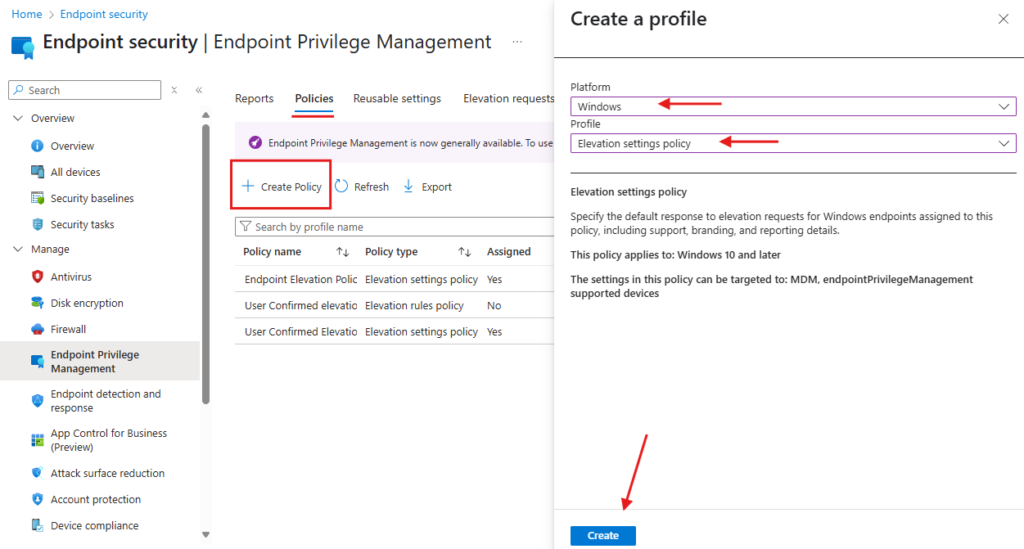
- Enter a Policy Name and Description, then click Next.
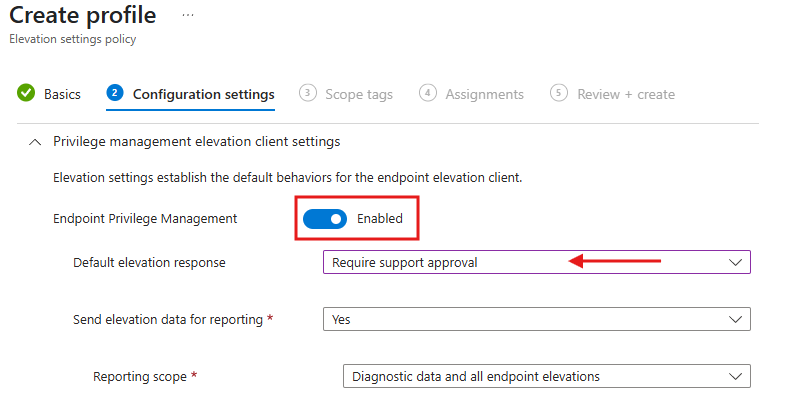
- Configure Settings
- In the Configuration Settings, enable Endpoint Privilege Management.
- Set the Default elevation response to Require support approval (as shown below).
- Assign Devices > Go to the Assignments tab.
- Assign the policy to all Intune-enrolled devices.
- Review and Create > Review the policy configuration and click Create.
End-User Experience: Elevating Privileges
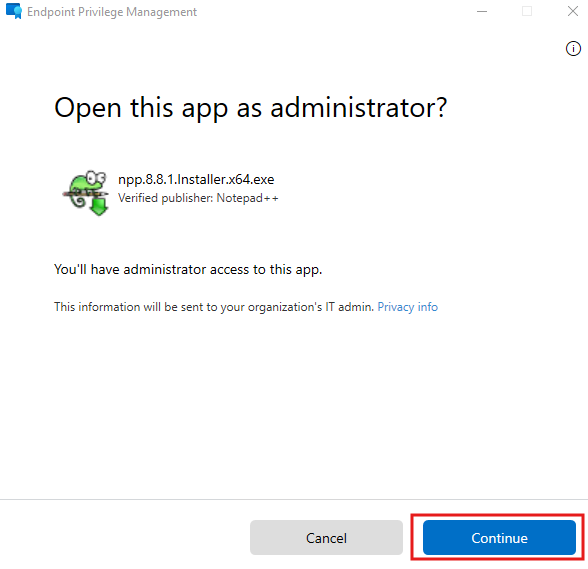
- The end user downloads software or an application from the internet.
- Right-click the downloaded app and select Run with elevated access.
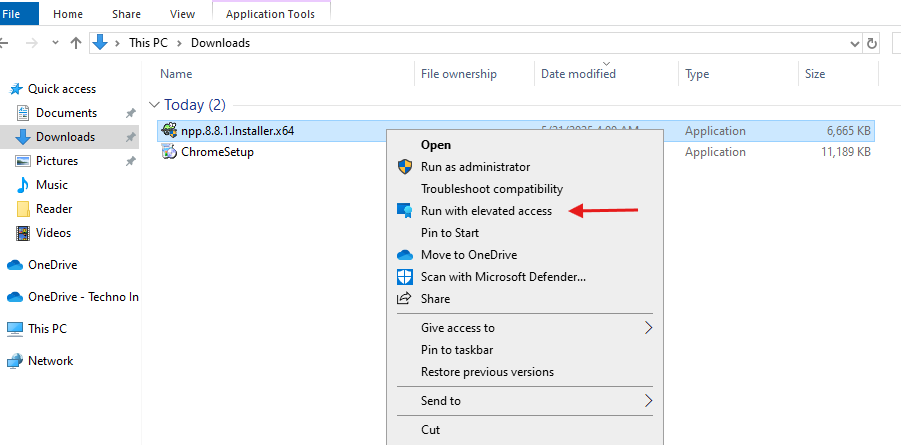
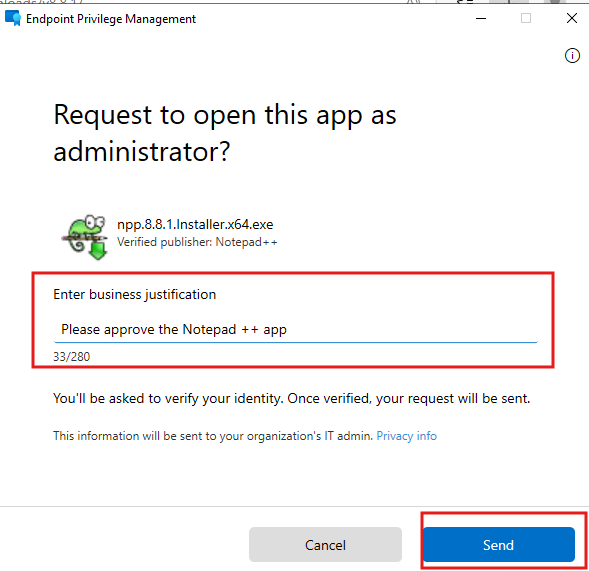
- A request window will appear where the user must provide a justification for the installation.
- Enter the justification and click Send.
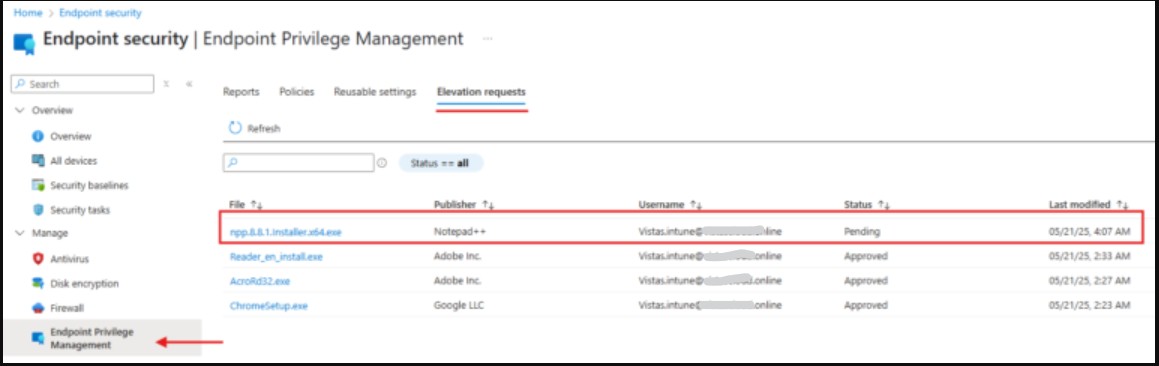
Admin Approval Process
- The Intune Administrator reviews the request by navigating to:
Endpoint Privilege Management > Elevation Requests.
- Open the request, select Approve or Deny, provide a reason, and click Yes.
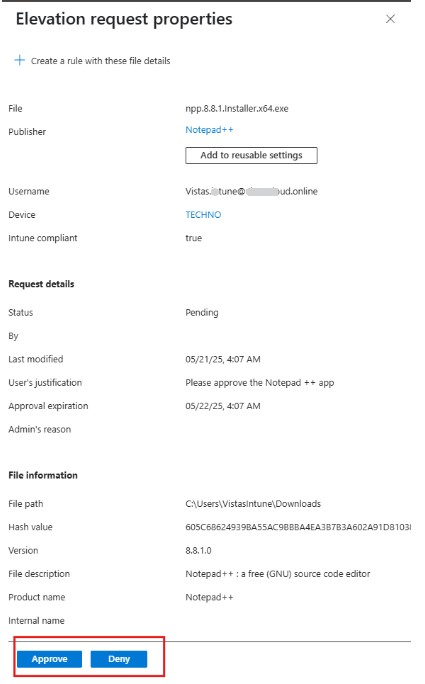
Once approved, inform the user that they can now install the app using Run with elevated access. This allows the user to install the application without needing to manually enter admin credentials.
Creating and Managing Elevation Rules
Rule Templates and Conditions
Set conditions like:
- App name
- Publisher
- File hash
- Path-based rules
Best Practices for Rule Creation
- Start with audit mode to see how users interact
- Avoid wildcard paths
- Target specific groups or departments
Common Use Cases for EPM
- Software Installation – Allow users to install approved tools without IT delay
- Temporary Troubleshooting – Helpdesk can grant time-limited admin rights
- Developer Access – Provide developers admin rights for specific tools only
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Native to Microsoft’s ecosystem
- Real-time auditing and reporting
- Easy to manage within Intune
Cons:
- Windows-only support (no macOS/Linux)
- Fewer customization options than some third-party privilege management tools
Security and Compliance Impact
- Fully aligns with Zero Trust principles
- Provides clear, exportable logs for audits
- Best practice: Configure the Elevation Response by Default Will Need Support Approval
Troubleshooting Tips
If policies are not applying:
- Verify device is Intune and Entra ID enrolled
- Check Intune sync status
- Confirm correct group targeting
For logs and reporting:
- Use Intune reports in Microsoft Endpoint Manager
- Check Event Viewer for local logs
Recommended Rollout Strategy
- Start with a pilot group
- Monitor usage and request trends
- Gradually expand deployment to the full organization
- Train users on request and approval workflows
FAQs
Q: Is EPM included with Intune by default?
A: No, it requires the Intune Suite or an EPM add-on license.
Q: Can users elevate their own permissions?
A: Yes, based on your configured policy — either auto-approved or requiring IT approval.
Q: Does EPM work on macOS or Linux?
A: No, only Windows 10/11 Enterprise and Education editions are supported.
Q: How do I monitor elevated actions?
A: Use audit logs and reports in the Intune Admin Center.
Final Thoughts
One effective strategy for maintaining a balance between security and productivity is to use Microsoft Intune’s Endpoint Privilege Management feature. By replacing permanent admin rights with temporary, controlled elevations, organizations can:
- Reduce security risks
- Improve compliance readiness
- Maintain user efficiency
Start with a pilot, refine your policies, and gradually roll out EPM across your organization to fully embrace least privilege without slowing down your workforce.
Related Links:
- Microsoft Intune Beginner Guide 2026: Everything you need to know
- Configure and Implementations of Microsoft Intune Policies
- Windows Autopilot Deployment: A Step-by-Step Guide 2026
- Step-by-Step Guide for Windows Devices Enrollment in Microsoft Intune
Enjoyed the article?
We’d love to hear your thoughts—share your comments below!
For more insights, guides, and updates from the Microsoft ecosystem, be sure to subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on LinkedIn. Stay connected and never miss out on the latest tips and news!




This was super helpful—thank you! We’ve just started rolling out EPM in our environment and I was trying to wrap my head around how the elevation requests actually work. Your explanation made it so much clearer. I’m hoping Microsoft adds more flexibility around approvals in the future, but for now, this is definitely a big step up from giving users full admin rights. Great stuff!
Really appreciate the kind words! Totally agree—EPM is still evolving, and more control over approvals would definitely be a welcome addition. Glad the post helped clarify things! Let us know how your rollout goes or if you run into anything interesting—we’re always keen to learn from real-world experiences. 🙌
This is a great overview! I’ve been curious about how Endpoint Privilege Management works in Intune — this post cleared up a lot.
Thanks for the kind words! We’re glad it helped clarify things. Let us know if you want us to cover any specific Intune features in future posts.
Very nice blog post. I definitely love this website. Keep it up!