
- February 8, 2025
- Pankaj Kumar
- 2
Data management is critical for organizations leveraging tools like Emails, Teams, SharePoint, and OneDrive. Imagine a situation where your business holds sensitive client emails, team collaboration documents, and project files. Without a clear data retention policy in place, managing this information becomes a challenge—leading to compliance risks, data breaches, and unnecessary storage costs. Implementing a retention policy helps businesses comply with legal regulations, improve data governance, and protect critical information.
A Data Retention Policy in Microsoft 365 ensures that data is retained only as long as necessary and securely deleted when no longer needed. This guide provides a step-by-step process for setting up retention policies in your M365 environment, discusses their importance, and answers common questions to help you manage your data lifecycle effectively.
What is a Data Retention Policy?
A retention policy defines how long data should be retained and when it should be deleted. These policies help organizations manage document and email lifecycles while ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
Why Enabling Retention Policies is Important
1. Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Many industries require businesses to retain data for specific periods to comply with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOX. A retention policy ensures compliance by automatically storing or deleting content as needed.
2. Preventing Data Loss and Accidental Deletion
Retention policies safeguard business-critical documents by preventing accidental or premature deletion. When applied, content is preserved in the Preservation Hold Library, ensuring no data loss.
3. Improved Data Governance and Organization
A well-defined retention policy helps businesses manage their data efficiently, ensuring that only relevant content is retained while outdated or unnecessary files are deleted.
4. Enhancing Security and Reducing Risks
By eliminating redundant or outdated data, retention policies reduce security vulnerabilities and prevent unauthorized access to outdated documents.
5. Cost Optimization and Storage Management
Over time, unused and redundant data increases storage costs. Retention policies help reduce storage consumption, optimizing SharePoint Online resources and minimizing unnecessary expenses.
How Retention Policies Help Organizations
1. Centralized Data Control
Administrators can define retention settings across multiple SharePoint sites, ensuring uniform compliance and governance.
2. Streamlined Legal Discovery and Audits
Retention policies simplify legal discovery by ensuring all necessary documents are preserved and easily retrievable when needed.
3. Automating Document Lifecycle Management
Organizations don’t have to manually track and delete old data. Retention policies automate the process, improving efficiency and accuracy.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Data Retention Policy in Purview Compliance Portal
Step 1: Access the Compliance Portal in Microsoft 365
- Sign in to your Microsoft 365 Admin Center.
- Go to the App Launcher and select Compliance to access the Microsoft Purview Compliance Portal.
Step 2: Navigate to Data Lifecycle Management
- In the left-hand menu, click Data Lifecycle Management.
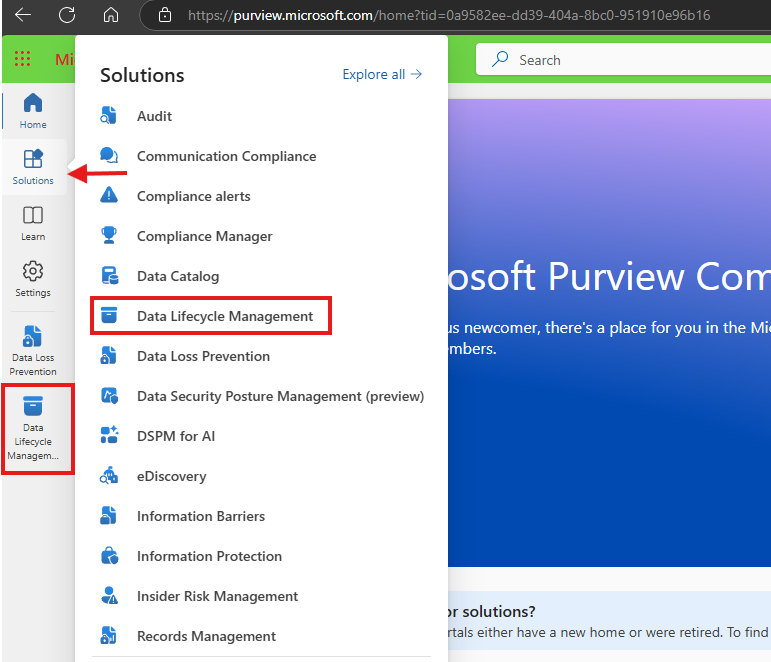
- Expand the Policies and Select the Retention Policies to manage retention settings.
- Click Retention Policies to view existing policies or create a new one.
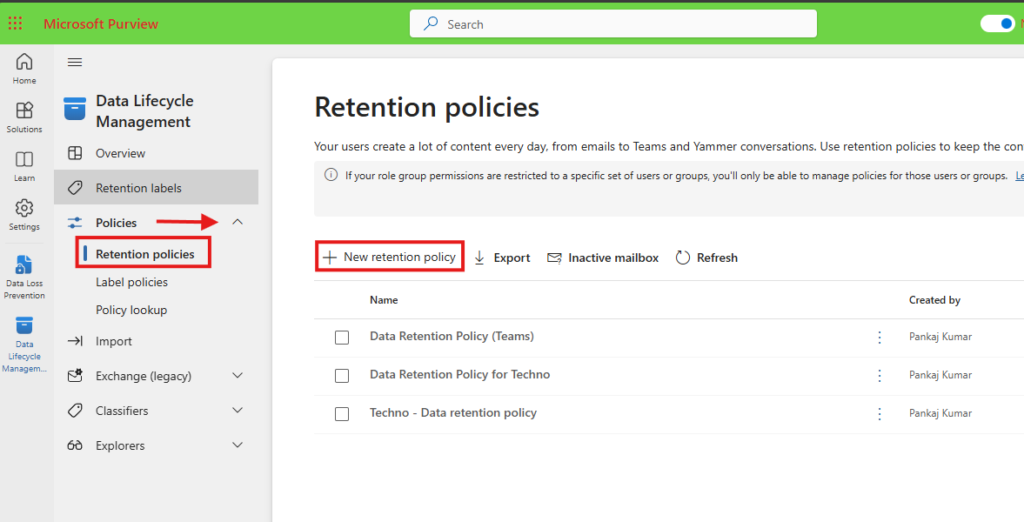
Step 3: Create a New Retention Policy
- Click New Retention Policy.
- Enter a clear and descriptive name for the policy.
- Add an optional description to define its purpose.
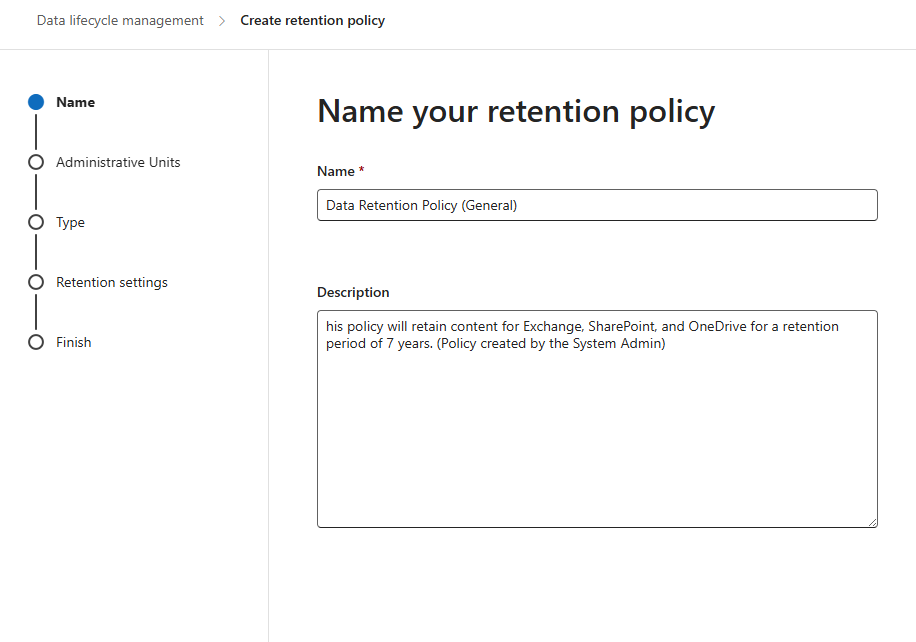
Step 4: Configure Policy Scope
- Choose between Static Scope (specific sites) or Adaptive Scope (dynamic rule-based targeting).
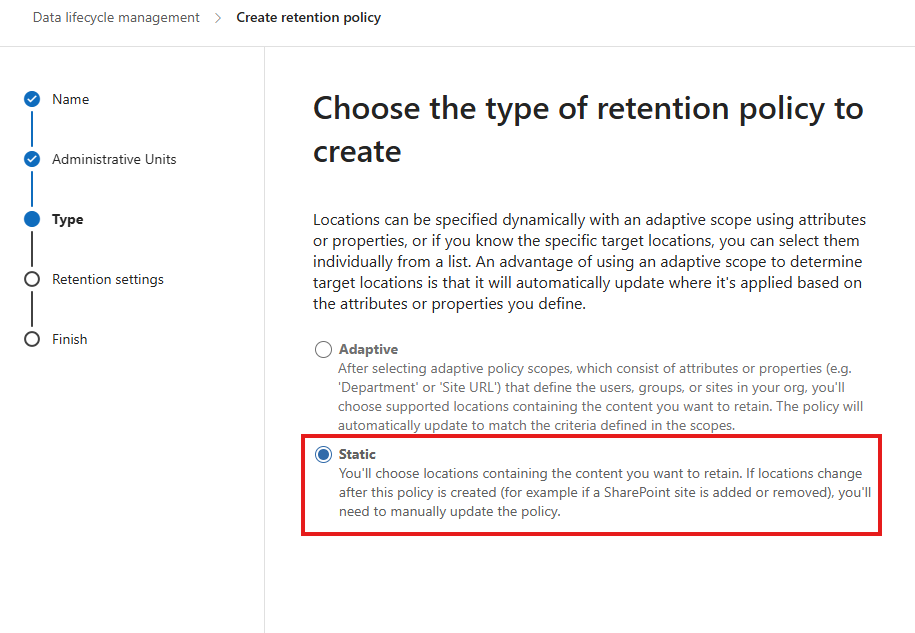
- Select Exchange Mailboxes, SharePoint Sites, OneDrive and M365 Groups and Sites and specify the URLs where the policy will apply.
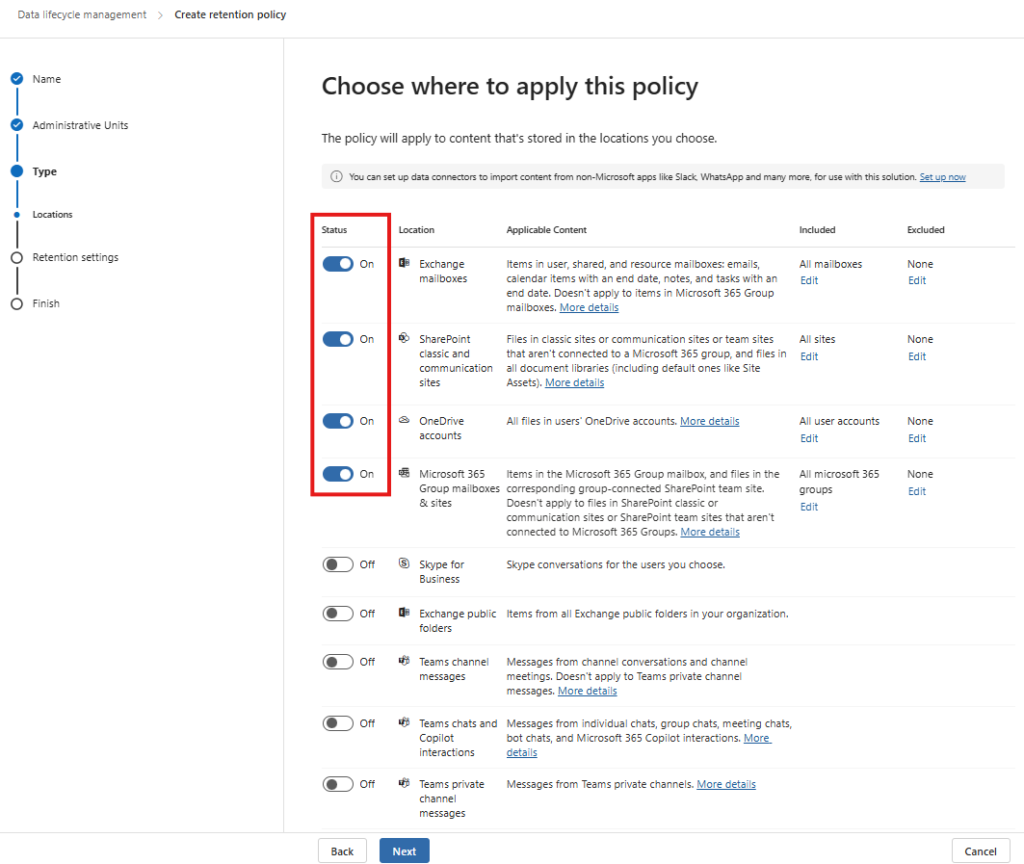
Note: A single retention policy cannot be created for both SharePoint and Teams emails, as Teams data is stored in different locations. While a retention policy can include multiple locations, SharePoint sites and Teams channels cannot be combined as a single location within the same policy. Therefore, separate retention policies are required to manage each platform individually.
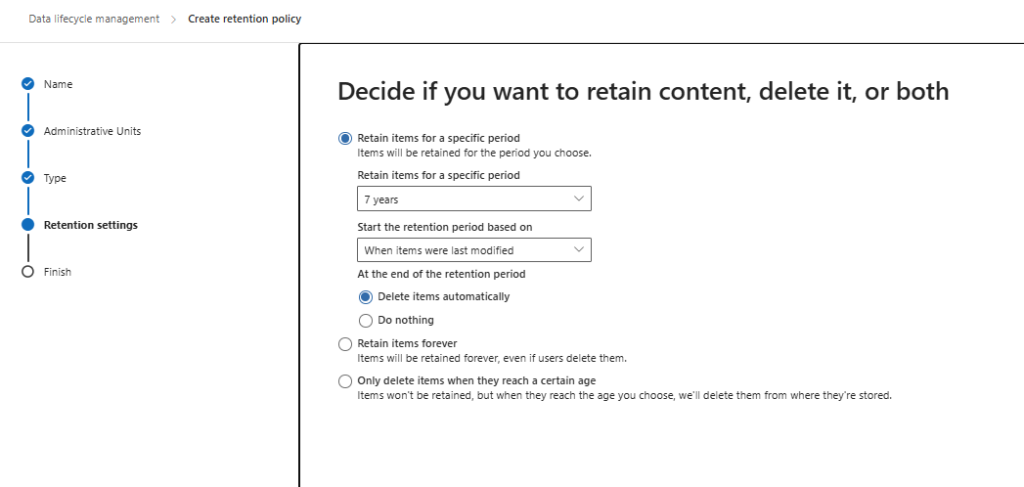
Step 5: Define Retention Settings
- Retention Period: Choose how long the data should be retained (e.g., 7 years).
- Retention Actions:
- Retain Only: Keep content but do not delete it automatically.
- Retain and Delete: Store content for the set period, then delete it.
- Delete Only: Automatically remove data after a specific period.
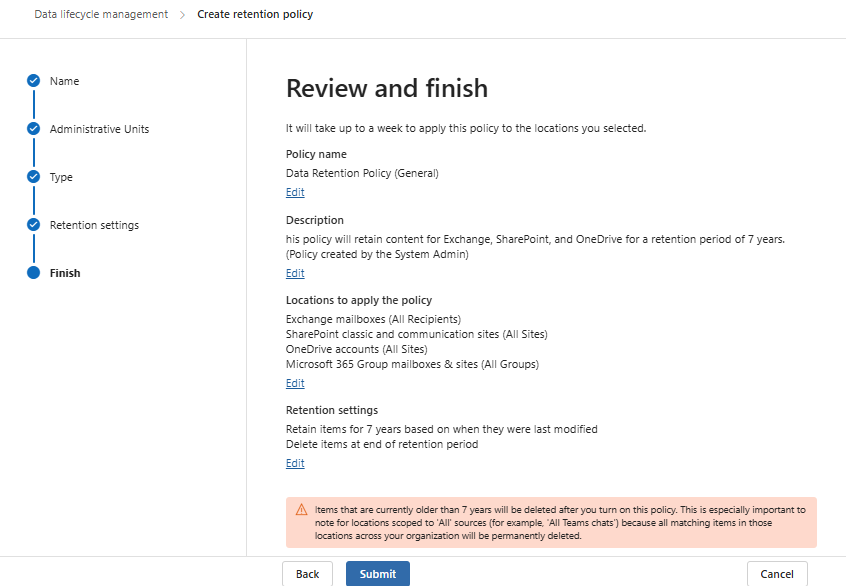
Step 6: Review and Finalize
- Check all configurations carefully.
- Click Submit and Create to activate the policy.
Effects of Applying a Data Retention Policy to a SharePoint Site
1. Restrictions on Deleting a SharePoint Site
Once a retention policy is applied to a SharePoint site, deleting the site becomes restricted. Whether attempting deletion through the SharePoint Admin Center or directly from the site, an error message will appear stating:
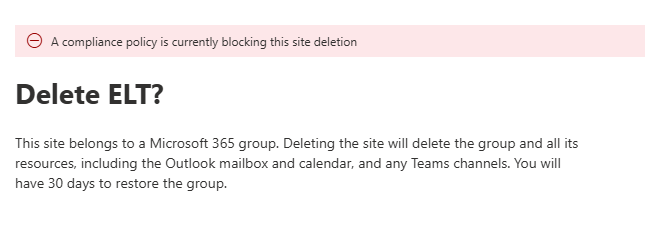
Error Messages:
- From SharePoint Admin Center – Users will encounter an error message preventing site deletion.
- From the Site Information Panel – A similar error will be displayed, restricting site removal.
2. Restrictions on Deleting Non-Empty Folders
Folders containing subfolders or files cannot be deleted while under a retention policy. An error alert will appear if you try to perform this:
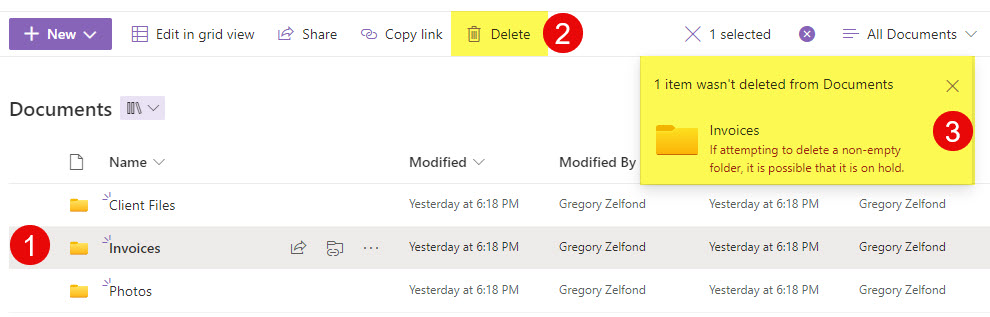
To remove the folder, all files and subfolders inside it must be deleted first.
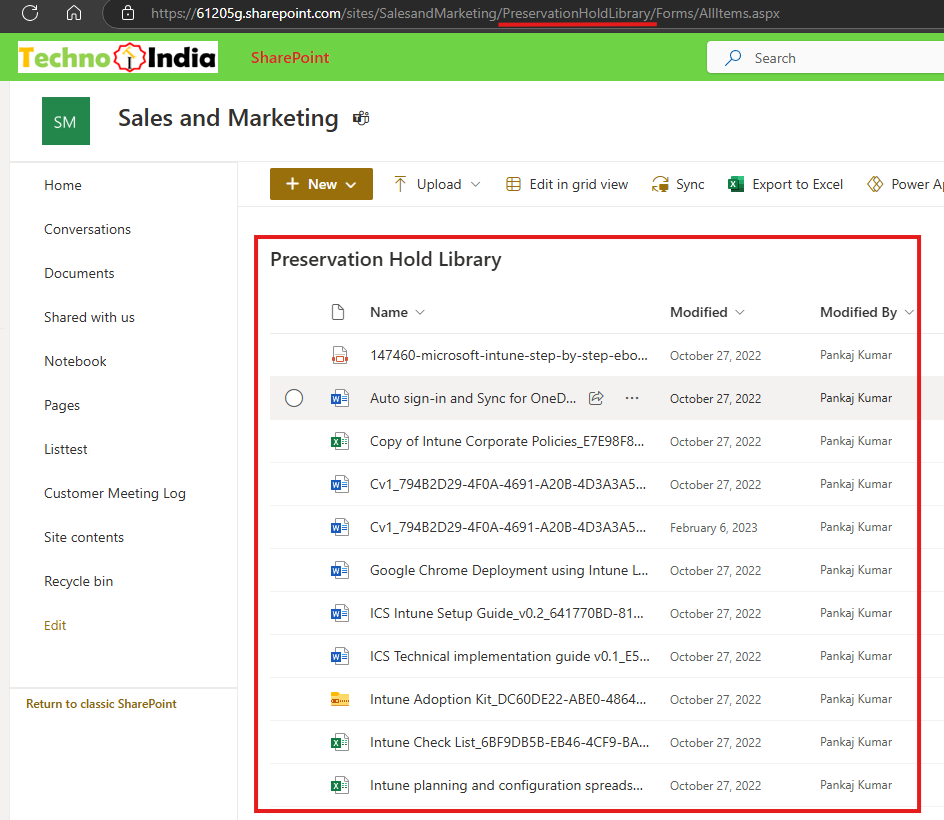
3. Creation of a Preservation Hold Library
When at least one document is deleted from a SharePoint site under retention, a Preservation Hold Library is automatically created. This special document library stores deleted files for the entire retention duration.
- The Preservation Hold Library is not visible under Site Contents.
- To access it, append the following to the site URL: /PreservationHoldLibrary
How Retention Works on a SharePoint Site
- During the retention period, deleted documents first go to the Recycle Bin. Simultaneously, a copy is placed in the Preservation Hold Library.
- Once the retention period expires, the document is permanently removed from the Recycle Bin.
This ensures compliance with data retention policies while providing a structured way to manage deletions within SharePoint.
Conclusion
Implementing site retention policies in SharePoint Online is essential for effective data governance and compliance. By following this guide, organizations can establish robust retention strategies that safeguard critical information, comply with legal requirements, and streamline data management processes.
FAQs
- What happens if I delete a document under a retention policy?
If a document is deleted while a retention policy is active, it is moved to the Preservation Hold Library instead of being permanently erased. - Can I apply multiple retention policies to the same SharePoint site?
Yes, multiple retention policies can be applied, but Microsoft 365 follows the rule of longest retention wins when conflicts arise. - How long does it take for a retention policy to apply?
It may take up to 7 days for a retention policy to fully take effect across all specified SharePoint Online sites. - Does a retention policy override SharePoint’s Recycle Bin?
Yes, even if a user deletes a document and it is removed from the Recycle Bin, a retention policy preserves the content in the Preservation Hold Library. - Can I edit an existing retention policy?
Yes, administrators can modify existing retention policies, but changes may take some time to reflect across the organization. - Does a Data retention policy apply to SharePoint sub-sites?
Yes, retention policies apply to all content within the selected SharePoint site, including sub-sites. - What permissions are required to create a retention policy?
You must have Global Administrator, Compliance Administrator, or SharePoint Administrator permissions to manage retention policies.
Related URLs:-
- Microsoft 365 Data Protection: The Ultimate Guide to Secure Your Cloud Data
- Secure Sensitive Documents in SharePoint Online Using IRM: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Create and Manage eDiscovery Cases in Microsoft 365: A Step-by-Step Guide.
- How to Send Encrypted Email in Outlook: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
- Microsoft Defender for Office 365: Your Shield Against Cyber Threats
Enjoyed the article?
We’d love to hear your thoughts—share your comments below!
For more insights, guides, and updates from the Microsoft ecosystem, be sure to subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on LinkedIn. Stay connected and never miss out on the latest tips and news!

















Great post. I am dealing with some of these issues as well..
Thanks for the kind words! Glad to hear the post resonated with you. If you’re facing any specific issues or need help with anything we covered, feel free to drop a question—I’m happy to help wherever I can!