
In today’s digital world, keeping your business compliant and preventing conflicts of interest is crucial. Microsoft Information Barrier (IB) is a powerful tool that helps control communication and collaboration between different user groups in Microsoft 365. Whether you work in financial services, Education, legal, or healthcare, Microsoft IB helps create “ethical walls” to stop insider trading, protect sensitive data, and keep information confidential.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about Microsoft Information Barrier. You’ll learn how it works, its key features, and how to use it in real-world scenarios. Plus, we’ll show you a step-by-step strategy to set it up and make your workplace more secure and compliant.
What is Microsoft Information Barrier?
Microsoft Information Barrier is a compliance feature in Microsoft 365 that restricts communication and collaboration between specific groups within an organization. It helps businesses meet legal, regulatory, and ethical requirements by preventing conflicts of interest and controlling information flow.
For example, in a financial services firm, employees working on mergers and acquisitions can be restricted from communicating with traders to prevent insider trading violations.
How Does Microsoft Information Barrier Work?
Microsoft Information Barrier operates within:
- Microsoft Teams
- SharePoint
- OneDrive
- Exchange Online
When configured, it enforces policies that:
- Prevent direct communication – Users in separate groups cannot chat, call, or schedule meetings.
- Restrict collaboration – Blocked users cannot add each other to Teams, SharePoint sites, or shared documents.
- Control visibility – Blocked users cannot see each other in searches or suggestions.
IB policies are configured using Microsoft Purview Compliance Center and enforced through Microsoft 365 Security & Compliance controls.
Microsoft Information Barrier Workflow
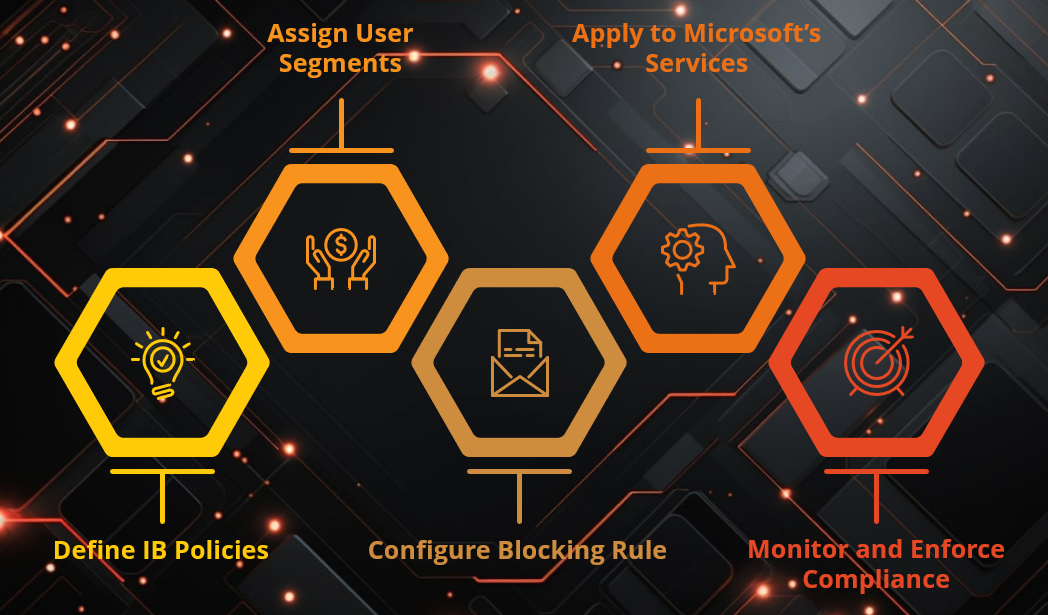
Key Features of Microsoft Information Barrier
- User Segmentation
- Define user groups based on departments, roles, and compliance needs.
- Blocked Communication Policies
- Set up rules to restrict chats, meetings, and calls between different user groups.
- Collaboration Restrictions
- Prevent unauthorized access to Teams, SharePoint, and OneDrive files.
- Compliance and Monitoring
- Track policy enforcement using Microsoft Purview Audit Logs and Microsoft Defender for Office 365.
- Integration with Microsoft 365 Compliance Center
- Easily manage and enforce IB policies across multiple Microsoft 365 services.
Use Cases of Microsoft Information Barrier
Day Traders and Marketing Team: Day trader group members should not be able to communicate or share files with the marketing team to prevent conflicts of interest and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Instructors and Students from Different Schools: Instructors from one school should not be able to communicate or share files with students from another school within the same school district to maintain privacy and prevent unauthorized information sharing.
Finance Personnel and Restricted Groups: Finance personnel handling confidential company information should be restricted from communicating or sharing files with certain groups within their organization to protect sensitive financial data.
Internal Teams with Trade Secrets: Internal teams working on trade secret material should not be able to call or chat online with specific groups within their organization to safeguard proprietary information.
Research and Product Development Teams: Research teams should only be allowed to call or chat online with the product development team to ensure controlled collaboration and protect intellectual property.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up Microsoft Information Barriers
Step 1: Enable Microsoft Information Barriers
-
- Ensure that your organization has Microsoft 365 E5, Office 365 E5, or Microsoft E5 Compliance add-on.
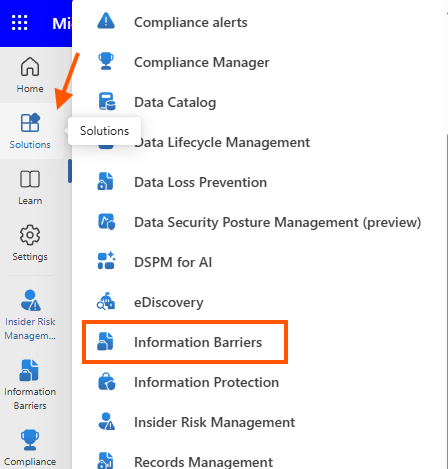
Step 2: Define User Segments
-
- Navigate to Information Barriers under the solutions.
-
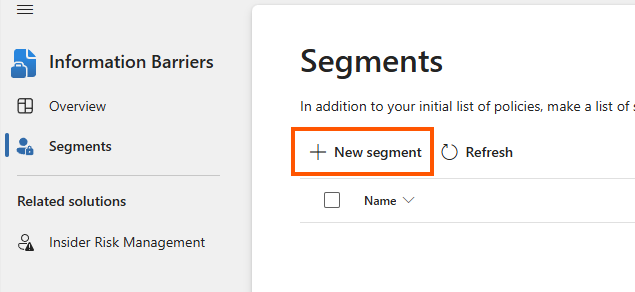
- Create segments to define user groups that should be blocked from communicating with each other
-
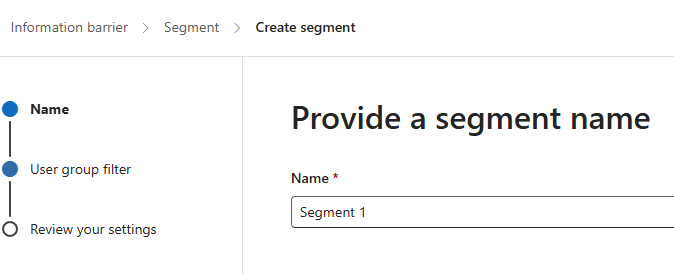
- Give each segment a name
-
- Specify filters to add users, preferably using the ‘Member of’ option for group-based segmentation. For better management, create dynamic groups
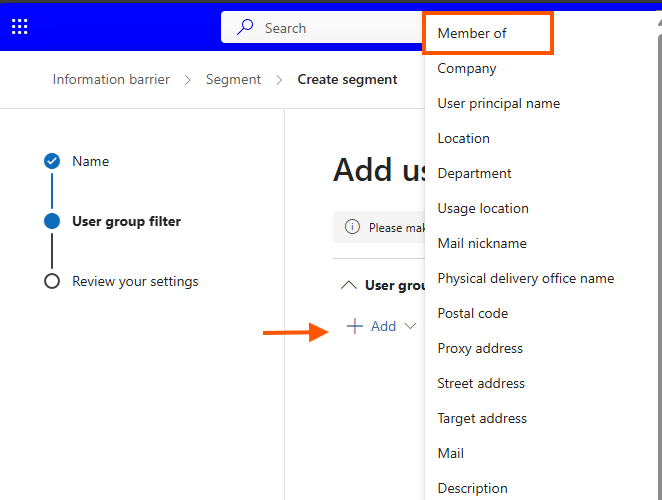
-
- Review and create the segment
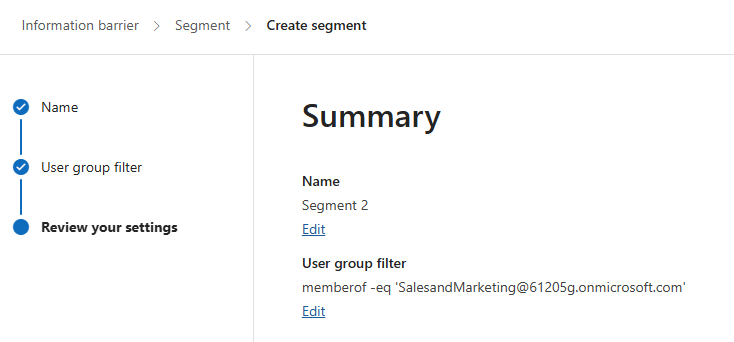
-
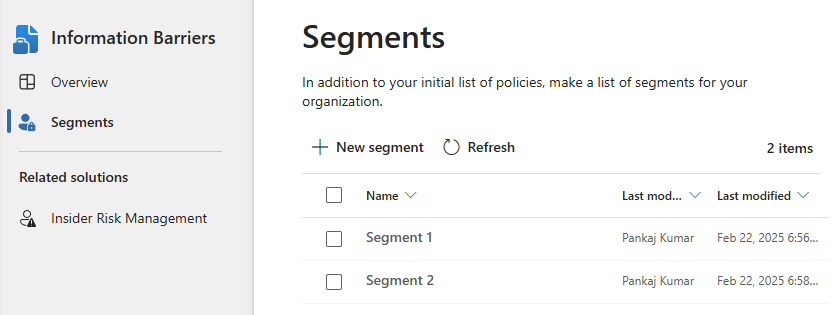
- Repeat the process to create a second segment
Step 3: Create IB Policies
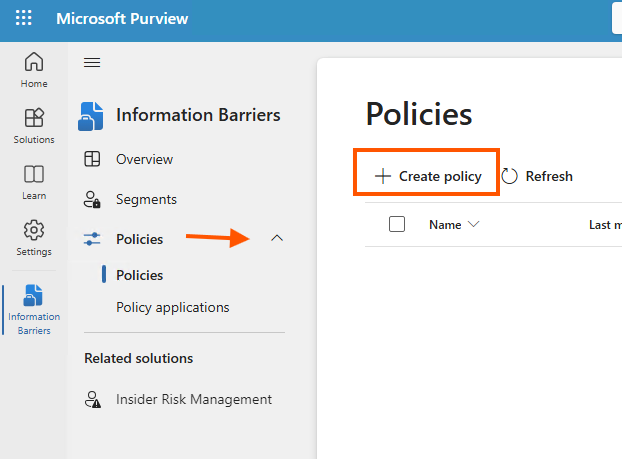
If you cannot locate the Policies option under Segments, use the link: “https://purview.microsoft.com/informationbarrier/policies?tid=0a95xxxxx-dd39-xxxx-8bc0-00000000″
(Replace tenant ID with your actual tenant ID).
-
- Alternatively, use PowerShell with the
New-InformationBarrierPolicycommand. New-InformationBarrierPolicy (ExchangePowerShell) | Microsoft Learn
- Alternatively, use PowerShell with the
-
- Enter the Policy Name and select the segments you created.
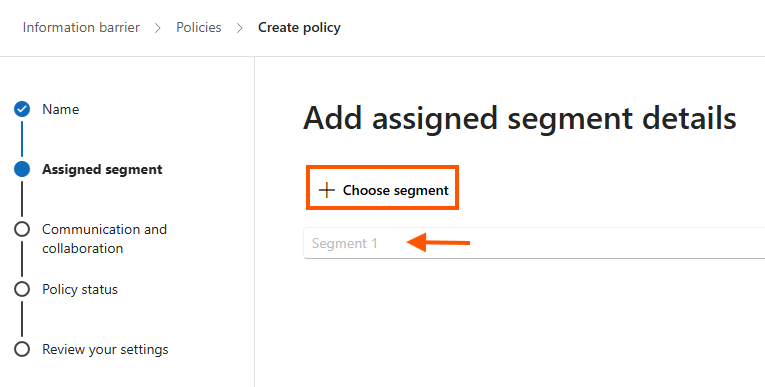
-
- Under Communication and Collaboration, select Allowed/Blocked and define restrictions between segments.

-
- By default, restrictions apply to Teams, SharePoint, and OneDrive. To restrict emails, create a separate Transport Rule in Exchange Online.
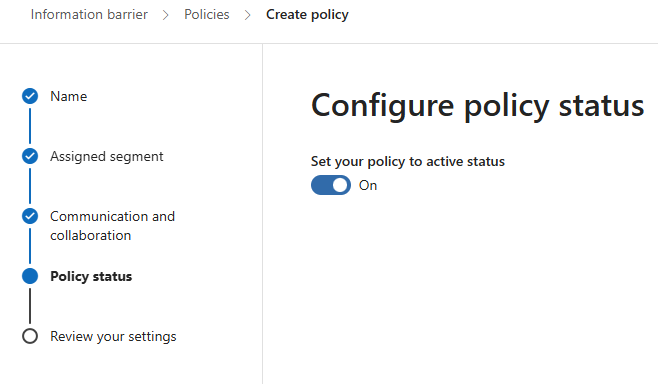
-
- Enable the policy and submit it.
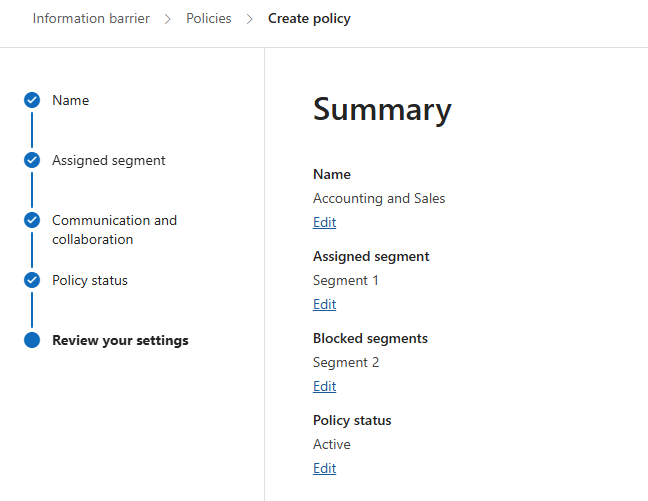
-
- Deploy the policy by navigating to the Policy Application Menu.
If the option is unavailable, try: “https://purview.microsoft.com/informationbarrier/applications?tid=xxxx-xxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxx” Replace the tenant ID with your tenant id.
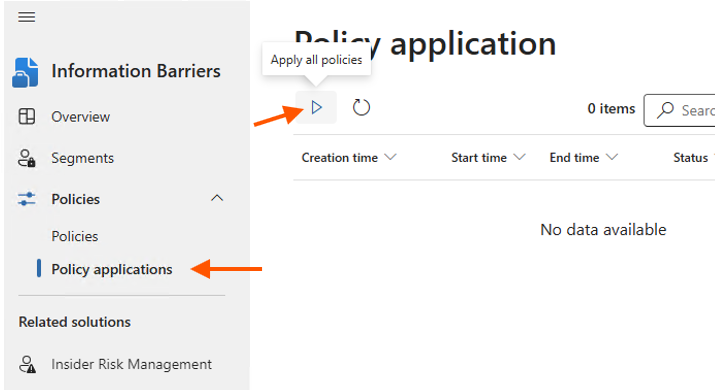
-
- If you encounter errors, retry after some time.

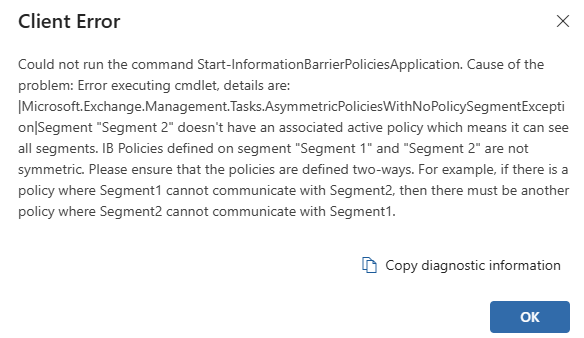
-
- After waiting for about an hour, you should see the deployment status as completed.
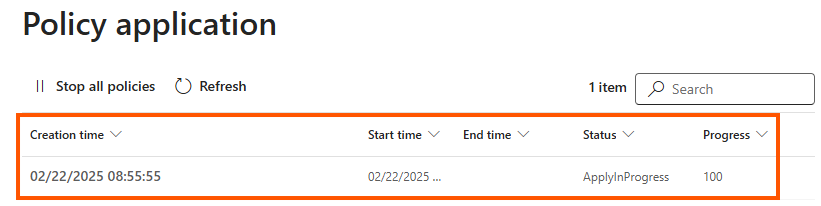
Step 4: Apply Policies to Microsoft 365 Services
-
- Test policies in a controlled environment
-
- Deploy policies across Microsoft 365 tenants
-
- Monitor policy effectiveness via Audit Logs
Step 5: Monitor and Update Policies
-
- Use Microsoft Defender and Purview Logs to track policy violations
-
- Modify policies based on organizational changes or compliance updates
Best Practices for Using Microsoft Information Barriers
- ✔ Regularly review and update IB policies to align with regulatory changes.
- ✔ Use Microsoft Defender for Office 365 to enhance security monitoring.
- ✔ Educate employees on compliance and ethical wall requirements.
- ✔ Test policies before full deployment to avoid disruptions.
Conclusion
Microsoft Information Barrier is an essential compliance tool that helps organizations restrict communication and collaboration based on regulatory and ethical requirements. Whether you work in finance, healthcare, or law, IB ensures data security, regulatory compliance, and ethical business operations.
By setting up and managing IB policies effectively, organizations can protect sensitive information, prevent conflicts of interest, and maintain compliance with global regulations.
FAQs
1. What Microsoft 365 licenses are required for Information Barriers?
You need Microsoft 365 E5, Office 365 E5, or the E5 Compliance add-on to access Information Barriers.
2. Can Information Barriers block external users?
No, IB policies are designed for internal users within the same Microsoft 365 tenant.
3. Does Information Barriers restrict file sharing?
Yes, IB can prevent users from sharing files via SharePoint, OneDrive, and Teams.
4. How can I monitor Information Barrier policies?
Use Microsoft Purview Audit Logs and Defender for Office 365 to track policy enforcement.
5. What happens if a policy conflict occurs?
Conflicting policies will be flagged in Microsoft Compliance Center, requiring admin review and resolution.
Relates URLs:-
- Secure Sensitive Documents in SharePoint Online Using Information Rights Management
- How to Setup Microsoft 365 Data Loss Prevention: A Comprehensive Guide
- Microsoft 365 Data Protection: The Ultimate Guide to Secure Your Cloud Data
- How to Create and Manage eDiscovery in Microsoft 365: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Microsoft Insider Risk Management: A Complete Guide to Prevent Insider Threats
Enjoyed the article?
We’d love to hear your thoughts—share your comments below!
For more insights, guides, and updates from the Microsoft ecosystem, be sure to subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on LinkedIn. Stay connected and never miss out on the latest tips and news!
















